Did you know that the femur is the longest bone in your body? Read about how femoral fractures are treated:
What are Femoral Fractures?
The femur is the long bone that connects the hip to the lower leg. It is the strongest bone in the body, but it unfortunately can fracture under certain conditions. A break in the femur bone is called a femoral fracture.
What causes Femoral Fractures?
The most common cause of a femoral fracture is direct trauma. The bone is very strong and therefore the force required to break it is rather strong. It is therefore seen in incidents such as road traffic accidents.
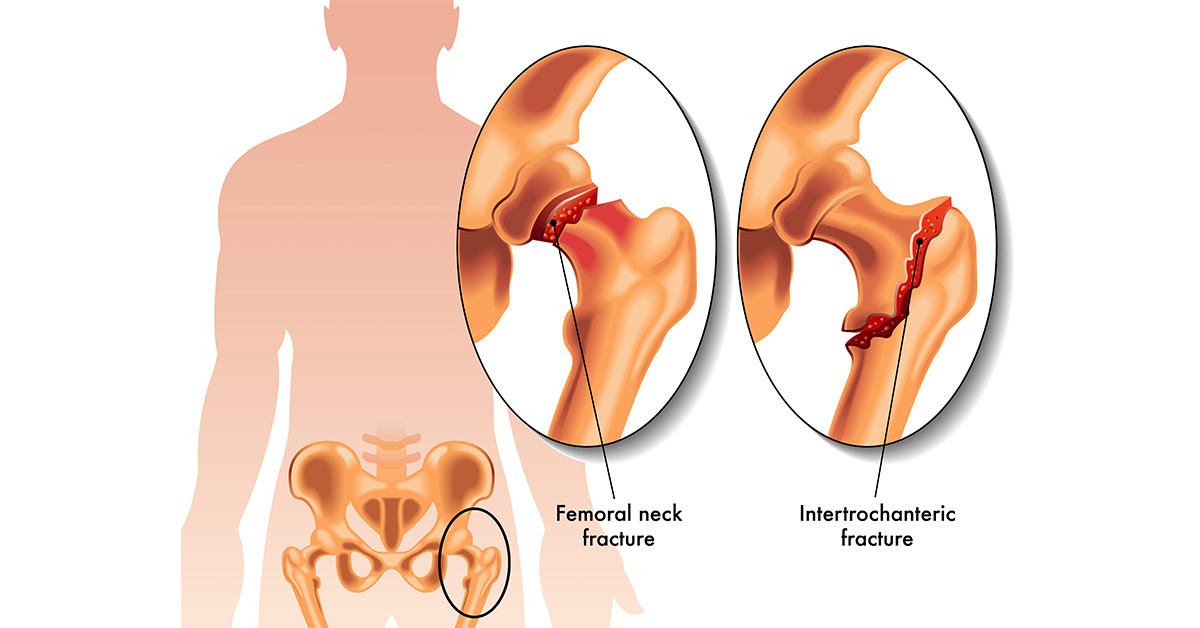
Fractures are classified according to their location, severity, and the pattern or direction in which they break. Depending on the location of the fracture, there are three classifications of femoral fractures:
- Proximal femoral fracture - this refers to fracture of the upper end of the femur
- Middle femoral fracture - this refers to the fracture around the middle of the femur
- Distal femoral fracture - this refers to fracture of the lower end of the femur
Depending on how the bone is broken, there are other types of femoral fractures as well. Here are some of the classifications used to describe femoral fractures based on pattern:
- Oblique femoral fracture - here the line a fracture is at an angle across the bone
- Comminuted fracture - this refers to multiple small fractures in one area of the femur
- Spiral fracture - this refers to a fracture that appears like a spiral around the femur
- Open fracture - this is where the bone is clearly broken and bone fragments project out of the skin.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The most common symptom of a femoral fracture is pain. This can be rather excruciating and patients will be unable to move the leg without experiencing pain. In cases of more proximal fractures, the length of the femur may be shortened, giving the leg an appearance of being shorter than the opposite one.
The most commonly used method to diagnose femoral fractures is a simple x-ray. This can help diagnose the type of fracture and can guide treatment. In some cases, a CT scan may be performed to get a better view.
How are Femoral Fractures treated?
Surgical treatment is usually the only option for femoral fractures. The type of surgery depends on the type of femoral fracture. In most cases, the broken ends of the bone will be realigned and pins may be put in place to keep the bone straight. Traction may be applied to the leg so that the bones may remain in one line and fuse properly.
The pins that are applied to keep the femoral bones in place may be applied through one of three techniques. The most common technique used is called intramedullary nailing. In intramedullary nailing, a surgical rod is inserted into the femur's marrow canal and across the fracture, keeping it secure. Plates and screws may also be applied to keep the fracture in place if intramedullary nailing can not be performed. If there are multiple injuries or if a temporary means of keeping the bones in place is needed before the patient can undergo a longer procedure, a procedure called external fixation may be used. In external fixation, a metal bar on the outside of the leg is connected to the pins and screws that are holding the fractured bone in place.
Complications of Femoral Fractures
Fracture of the femur can cause injury to the surrounding tissues. The sharp ends of the bones may injure the blood vessels and nerves causing bleeding and loss of sensation. The accumulation of blood and fluid within the muscles can increase the pressure within the leg and cause severe pain. This is called acute compartment syndrome and requires immediate treatment. Infections may occur, especially in open fractures, and require antibiotic treatment.
Rehabilitation
Following treatment for femoral fractures, patients require a course of physical therapy to help them weight bear on the affected leg and regain their mobility.